Skli.ai doesn't replace teachers—it amplifies their impact by handling information overload so they can focus on human connection.
Skli.ai uniquely excels in the Research and Understanding Phase of knowledge work—where other AI systems merely generate content, we specialize in breaking down complex information into structured, comprehensible formats. Our platform transforms uploaded texts and videos into customized learning resources: comprehensive summaries, intuitive mind maps, targeted flashcards, organized learning notes, and relevant study questions.
This is a second article in our SKLI.ai Deep Dives Series: Navigating the intersection of AI and curriculum development.
Introduction: Analyzing Two Foundational Educational Frameworks
This article provides a detailed analysis of two pivotal works in modern education theory and their intersection: Trilling and Fadel's "21st Century Skills: Learning for Life in Our Times" (2009) and Holmes, Bialik, and Fadel's "Artificial Intelligence in Education: Promises and Implications for Teaching & Learning" (2019). SKLI.ai's Mind Map function transforms educational texts into actionable insights that bridge theory and practice, offering a deeper understanding of how these frameworks complement and extend one another.
As artificial intelligence continues to transform industries worldwide, the education sector faces a critical inflection point. According to a recent Gartner report, over 45% of US educational institutions plan to implement AI-driven learning platforms by 2025. Similarly, the European Commission's Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027) has prioritized AI development in education, with €9.2 billion allocated to digital education initiatives including AI across EU member states. Switzerland, while not an EU member, has established itself as a leader in educational AI research through initiatives like the Swiss EdTech Collider at EPFL and the Swiss AI Education Initiative, which connects over 30 universities and research institutions focused on responsible AI integration in learning environments. Despite these investments, significant questions remain across all regions about how these technologies will shape what and how students learn.
SKLI.ai's Dual Analysis Approach: Mind Map Visualization and Comparative Analysis
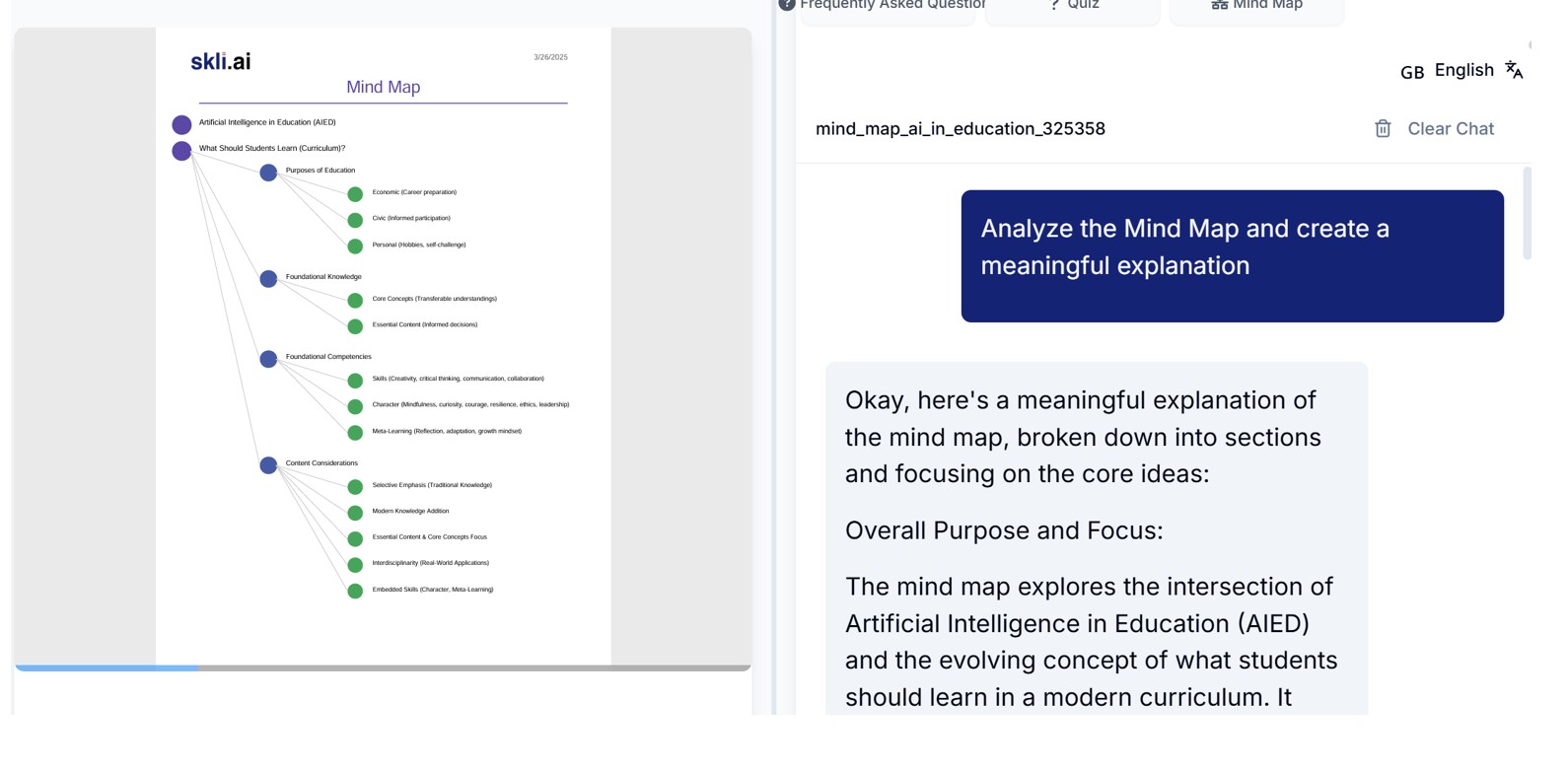
Our analysis process using SKLI.ai involved two key steps that demonstrate the platform's versatility in educational content analysis. First, we used SKLI.ai's Mind Map function to visualize the key concepts from "Artificial Intelligence in Education," creating a hierarchical representation of the book's complex ideas. This visual organization revealed relationships between concepts that might not be immediately apparent through traditional reading.
We then engaged with SKLI.ai's chat function to analyze how these mind-mapped concepts relate to the established framework in Trilling and Fadel's "21st Century Skills." This comparative analysis revealed both continuity and evolution in educational thinking over the decade between publications. The combination of these approaches allowed us to extract deeper insights, revealing how the authors' thinking on educational frameworks has developed in response to technological advancements while maintaining core principles about effective learning.
The Parallel Frameworks: Skills for an AI-Augmented World
The mind map reveals four key areas where AI in Education (AIED) aligns with and extends the 21st Century Skills framework, demonstrating both continuity in educational thinking and evolution in response to emerging technologies.
Foundational Competencies: Beyond Traditional Knowledge
Both frameworks emphasize a shift beyond traditional knowledge acquisition to essential competencies that prepare students for a rapidly changing world. The mind map highlights creativity, critical thinking, communication, and collaboration—directly mirroring the "4Cs" from Trilling and Fadel's framework. These skills become even more crucial in an AI context, as they represent uniquely human capabilities that complement rather than compete with AI systems.
The mind map extends beyond the 21st Century Skills framework by emphasizing character attributes like mindfulness, curiosity, courage, resilience, ethics, and leadership. These qualities become increasingly important as AI systems handle more routine tasks, placing greater value on distinctly human qualities. Both frameworks stress the importance of "learning how to learn" through reflection, adaptation, and growth mindset—skills that enable lifelong learning in rapidly changing environments.
Content Considerations: Modernizing Curriculum
The mind map outlines critical content considerations that align with and expand upon Trilling and Fadel's work. As AI makes information increasingly accessible, both frameworks advocate for careful selection of essential content rather than comprehensive coverage. The focus shifts from memorization to understanding core concepts and principles.
The mind map emphasizes "Real-World Applications" through interdisciplinary learning—a core principle in the 21st Century Skills framework that becomes even more relevant in an AI-augmented world where traditional subject boundaries are increasingly blurred. Additionally, the mind map advocates for curriculum updates that include contemporary fields like data science, AI ethics, and digital citizenship — areas that have become essential in today's educational landscape.
Addressing Common Challenges
Both frameworks identify similar challenges that education must address to remain relevant and effective. The accelerating transformation of job markets and skill requirements necessitates adaptable learning approaches that prepare students for careers that may not yet exist. With access to virtually unlimited information, discernment and critical evaluation become essential skills, requiring a shift from information acquisition to information evaluation and application.
Both frameworks emphasize the importance of applying learning across contexts rather than memorizing isolated facts. This focus on knowledge transfer becomes even more crucial in an AI-rich environment where factual information is readily accessible, but the ability to apply that information meaningfully remains a uniquely human strength.
Ethical Considerations: The AIED Extension
The mind map inspired by "Artificial Intelligence in Education" significantly extends the 21st Century Skills framework by directly addressing ethical implications of AI in education. It raises important questions about data privacy and ownership, considering who controls student data and how it's used. The map also highlights concerns about algorithm bias and the risk of perpetuating or amplifying existing inequities through AI-driven educational tools.
Student agency emerges as another critical ethical consideration, with the mind map warning about the risk of AI systems diminishing student autonomy and choice. Finally, it acknowledges the potential loss of essential interpersonal aspects of education as AI plays an increasingly prominent role in learning environments. These ethical dimensions represent one of the most significant ways the AIED framework builds upon and extends the earlier 21st Century Skills model.
The Distinct Contribution of AIED to Modern Education
The mind map reveals several ways AIED expands upon traditional 21st Century Skills frameworks, reflecting the rapid technological changes that have occurred since the original framework was developed.
AI as Both Tool and Subject
Unlike earlier educational technology frameworks, AIED positions artificial intelligence as both a learning tool and a subject to learn about. As a tool, AI enables applications like intelligent tutoring systems, exploratory environments, and automated assessment that can personalize and enhance learning experiences. As a subject, understanding AI techniques, limitations, and ethical implications becomes an essential part of modern literacy, preparing students to engage critically with the technology that increasingly shapes their world.
Specific AI Applications in Learning
The mind map details concrete applications of AI in education that weren't part of the original 21st Century Skills framework. Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) provide personalized, step-by-step guidance that adapts to individual student needs. Dialogue-Based Tutoring facilitates natural language interactions for learning, creating more engaging educational experiences. Exploratory Learning Environments create adaptive spaces for discovery that can adjust to student interests and abilities. Automated Writing Evaluation offers immediate feedback on written work, allowing students to iterate and improve more quickly than traditional assessment approaches.
The Framework of Modern Education
The mind map emphasizes that AIED must operate within a comprehensive educational framework that builds versatile education with broad and deep understanding. It focuses on robust foundations to prepare for uncertain futures rather than narrow skills that may quickly become obsolete. The framework develops deeper learning goals that transcend simple knowledge acquisition, recognizing that understanding principles and developing critical thinking are more valuable than memorizing facts in an AI-rich environment. Finally, it balances transfer with expertise to ensure both breadth and depth, preparing students to apply knowledge flexibly while still developing areas of specialized knowledge.
Practical Implementation: Bridging Theory and Practice
For educators and administrators implementing AI, SKLI.ai's analysis suggests several key considerations that connect theoretical frameworks to practical classroom applications.
Align AI with Educational Purposes
The mind map highlights three distinct purposes of education that AI must support. Economic preparation involves developing career-relevant skills that will remain valuable in an increasingly automated workforce. Civic participation fosters informed, engaged citizenship capable of critically evaluating information and participating meaningfully in democratic processes. Personal fulfillment encourages self-challenge and lifelong learning, recognizing that education extends beyond vocational training to encompass holistic human development.
Balance AI Efficiency with Human Connection
A critical tension identified in the mind map is the potential loss of human connection in teaching. Successful AI implementation requires preserving meaningful teacher-student relationships that foster not just intellectual but social and emotional development. Rather than replacing human interaction, AI should enhance it by handling routine tasks and freeing educators to focus on higher-order teaching. This ensures technology serves educational goals rather than dictating them, maintaining human values at the center of the educational enterprise.
Prioritize Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration
The mind map emphasizes the essential role of collaboration between various stakeholders in the educational ecosystem. Educators who understand learning needs must work alongside technologists who create AI systems to ensure tools are pedagogically sound. Policymakers who establish guidelines need input from both educators and technologists to create frameworks that encourage innovation while protecting student interests. Students whose learning is directly affected should have a voice in how AI is implemented, ensuring their needs and perspectives shape technological adoption.
SKLI.ai's Mind Map Function: Transforming Book Analysis into Visual Insights
The mind map analysis demonstrated in this article showcases how SKLI.ai's Mind Map function transforms traditional book analysis into powerful visual frameworks. By applying this tool to Holmes, Bialik, and Fadel's "Artificial Intelligence in Education," we've created a comprehensive visual representation that reveals connections, hierarchies, and relationships that might otherwise remain hidden.
Our Mind Map function helps educators, administrators, and students visualize complex educational frameworks and their interrelationships from source texts. It extracts actionable insights that might be distributed across different chapters or sections, making it easier to grasp the big picture. The tool identifies connections between seemingly disparate concepts within educational literature, revealing patterns and relationships that might be missed in linear reading.
Educators can create shareable visual resources that make complex books accessible to wider audiences, facilitating professional development and collaborative planning. Finally, the Mind Map function supports the development of implementation plans based on a holistic understanding of research-backed approaches, bridging the gap between theory and practice.
The Mind Map function represents just one of SKLI.ai's powerful tools for educational analysis. By transforming dense academic texts into clear visual frameworks, SKLI.ai empowers education professionals to extract maximum value from important works like "Artificial Intelligence in Education" and apply these insights to curriculum development with confidence.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Education with AI
The integration of AI in education represents both tremendous opportunity and significant challenge. As the mind map illustrates, successful implementation requires balancing innovation with educational fundamentals, technical capabilities with ethical considerations, and efficiency with human connection.
By understanding the relationship between AI applications and 21st century skills, educators can develop curriculum and teaching approaches that prepare students not just to exist alongside AI, but to thrive in a world increasingly shaped by it. The key lies in viewing AI as a powerful tool to enhance human potential rather than replace human capabilities.
The mind map demonstrates that the most promising path forward combines the best of both worlds: leveraging AI's capabilities to develop the uniquely human skills, character traits, and meta-learning abilities that will remain essential in an automated future.
References
[1] Gartner. (2023). Top Technology Trends in Higher Education for 2023. Gartner Education Practice Report. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/en/industries/education
[2] European Commission. (2021). Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027). Retrieved from https://education.ec.europa.eu/focus-topics/digital-education/action-plan
[3] Swiss EdTech Collider. (2023). AI in Education Initiative Report. École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL). Retrieved from https://edtech-collider.ch
[4] Holmes, W., Bialik, M., & Fadel, C. (2019). Artificial Intelligence in Education: Promises and Implications for Teaching & Learning. Center for Curriculum Redesign, Boston, MA.
[5] Trilling, B., & Fadel, C. (2009). 21st Century Skills: Learning for Life in Our Times. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, CA.
This article is the second in our "SKLI.ai Deep Dives" series, connecting timeless educational wisdom to today's most pressing challenges.